|
Listen to this article
|
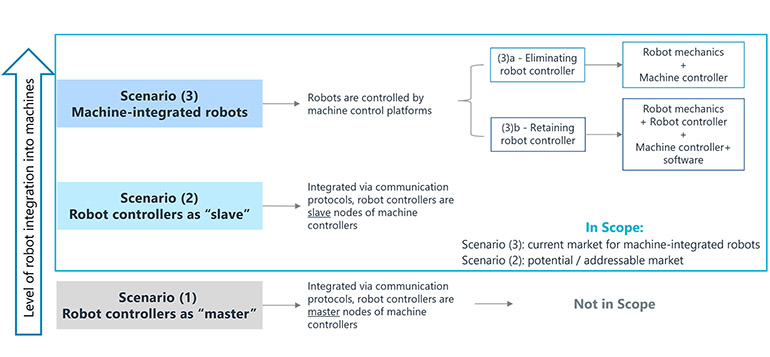
Interact Analysis identified three main scenarios for machine-robot integration. | Source: Interact Analysis
The market for machine-integrated robots is gaining momentum, according to Interact Analysis. The market research firm predicted steady growth for the market over the coming years, despite slow growth in the overall market for industrial automation.
Interact Analysis also noted that robotics and automation vendors have announced an increasing number of partnerships to develop new products, further driving growth in the market. It predicted that shipments of machine-integrated robots will grow steadily by 9.2% in 2024.
Over the next five years, the U.K.-based company said it expects the market to experience accelerated growth, even as the industrial automation space matures. It forecast a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.7% from 2024 to 2029, with North America and Europe leading the market.
Labor concerns drive interest in machine-integrated robots
Interact Analysis defined “machine-integrated robots” as robots that are governed by machine controls. Such robots emerged as a result of efforts to unify controls of machines and robots, primarily by eliminating robot controllers.
However, there is also the option of retaining robot controllers and programming the robots directly using machine controllers through software platforms.
“We see this growth potential primarily driven by the ongoing shortage of robot programmers and engineers, as dedicated robot programming languages are no longer required for machine-integrated robots,” wrote Samantha Mou, a research analyst at Interact Analysis.
“In addition, as machine builders, automation solution providers, and robot manufacturers continue to cooperate in this segment, the number of integrated solutions available on the market is increasing,” she said. “This will also accelerate the market growth of machine-integrated robots.”
To address the growing demand, both robot vendors and machine OEMs are manufacturing systems for machine-integrated robots. For each type of robot — articulated, cartesian, collaborative, delta, and SCARA — machine builders develop and make make the mechanics in-house. Many of OEMs even build customized kinematics, noted Mou.
In the meantime, robot vendors are offering models that support machine-integrated robot control. Manufacturers of industrial automation and motion-control products are the most active participants in this emerging market, said Interact Analysis. They are cooperating with robot vendors to promote integrated control systems to machine OEMs as well as systems integrators.
Partnerships are key for machine-integrated robots
Over the past five years, collaboration among machine and automation providers has accelerated.
For example, in April, Siemens said it is integrating its PLCs with collaborative robots from Universal Robots and Jaka. Cobots from both vendors now support the Standard Robot Command Interface (SRCI), enabling robot programming via Siemens PLCs.
In 2023, Rockwell Automation signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with Doosan Robotics, a Korean collaborative robot vendor. Doosan is working to integrate its robot control into Rockwell’s Logix system.
If the duo’s cooperation is successful, Doosan may allow integrated control of its cobots without dedicated robot controllers, Interact Analysis said.
Robot vendors work to integrate controls
In 2022, Beckhoff Automation launched its Automation Technology for Robotics, or ATRO. The industrial system enables machine builders and integrators to build modular robots integrated into the company‘s control platform.
Savage, Minn.-based Beckhoff has been active in building an ecosystem for integrated control of machines, robotics, vision, safety, and other functions.
In recent years, many industrial automation manufacturers have launched systems for machine-integrated robots, said Interact Analysis. For example, Omron released an integrated controller. Both SEW Eurodrive and Lenze have introduced specialized kits for OEM-made delta robots.
This year, Schneider Electric launched new collaborative robots with controllers that unify PLC, motion, and robotic control functions. It extended its machine-integrated offerings from industrial robots to cobots, said Interact Analysis.
The company said the machine-integrated robot market presents a new opportunity for component suppliers. Robotics vendors can enlarge their customer base and supply industries that robots with dedicated controllers cannot access.
Where machine builders are concerned, in addition to the time savings from integrated systems, integrating OEM-made robots with machine controllers could be more practical, said Interact Analysis. By building robot kinematics in house to address customized demand, they could create more unique selling points (USPs) for their products, it added.
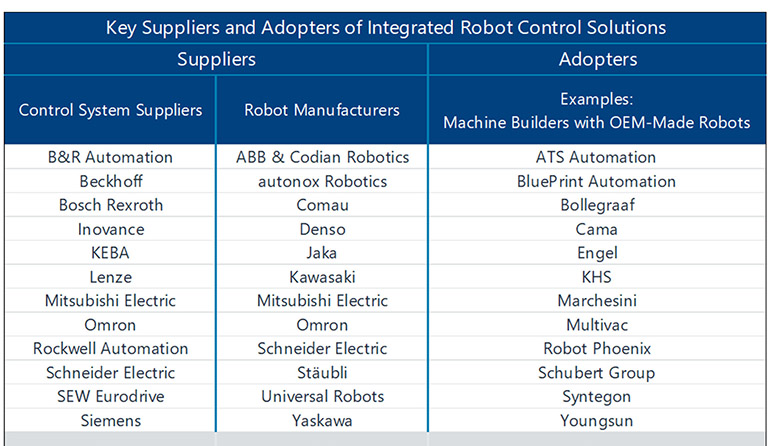
Many motion-control vendors, robot manufacturers, and machine builders have launched machine-integrated robots. | Source: Interact Analysis






Tell Us What You Think!